Categories
- Wire & Cable
- Multi-conductor & Signal Cable
- Battery Cable Assemblies
- Terminals and Connectors
- Electrical Parts
- Electrical Tools
- ID Products
- Wire Management
- Tape & Sealant
- Mounting Panels & Panel Blanks

Need Help?
Click HereGet a Business Account
Apply HereFuses and Fuse Blocks
What are Fuses?
![]()
Fuses are safety devices that are designed to sacrifice themselves in order to protect equipment from over current. That is to say, that fuses are an intentional weak link in an electrical circuit. A weak link that is designed to break if a power surge occurs before that surge can reach expensive or sensitive equipment. They are similar in a sense to breakers except that a breaker can be reused multiple times whereas a fuse can only be used once. For the most part, fuses are essential in electrical circuits for the protection function they provide and the safety that they offer.
"fuses are essential in electrical circuits for the protection function they provide and the safety that they offer."
What are fuse blocks?
![]()
A fuse block is a device that distributes power to multiple circuits and houses a fuse for each of those circuits. In this way, a fuse block is a gatekeeper where a surge cannot pass. Instead of having fuses all over the place for each circuit, a fuse block allows you to consolidate those fuses into one centralized location. Fuse blocks are available in a variety of sizes in styles to meet the needs of the different types of fuses we offer. One question we frequently hear is about the different types of fuses that we offer.
Where would a fuse and fuse block be implemented?

A fuse block is essential to nearly any electrical system
A fuse block would be implemented in applications where equipment needs to be protected from electrical spikes. They are a common part of the marine industry found on many boats. All Pacer fuses and each fuse block is perfect for new installs as well as when replacing equipment on your boat. If you have burnt fuses or a damaged fuse block, then these are the perfect parts for you. All you will need are the correct wire and the correct terminals. Now, let us shift our focus to the types of fuses that are available.
What types of fuses are available?
There are a variety of fuses to handle the different electrical needs out there and as such, we carry a range of them from the most popular to the more obscure. This way you can find the exact fuse you need to get your project done ahead of schedule. Below we will take a look at each of the different types of fuses and each fuse block that we carry and where you might use them.

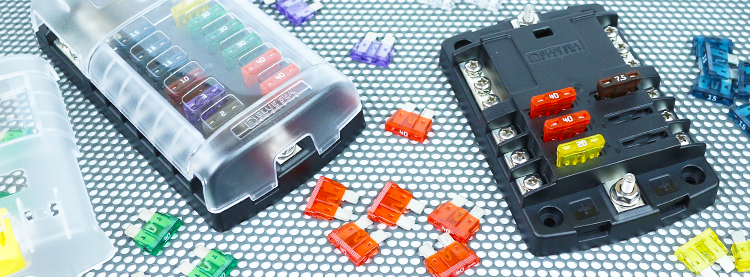
AGC
AGC, or automotive glass cartridge fuses, are fast acting fuses that gained popularity in the automotive industry. They are so fast acting that it is what they are mainly known for. Available in amperages from 0.5 amps to 30 amps, these are a solid choice for a range of electrical circuits.

ANL
ANL fuses are silver plated and offer a visible indication of when they are blown. ANL fuses are available in amperages ranging from 35 amps all the way up to 600 amps meaning that you can find the level of protection that is right for your application. This type of fuse is known for its simplistic installation.

ATC
ATC fuses are easily identifiable due to their prong type blades that are used for insertion into an electrical circuit. ATC fuses first appeared around 1976 and have become commonplace since then. This type of fuse is available in amperages ranging from 1 amp all the way to 40 amps.

Maxi
Maxi fuses are fast acting fuses that look quite similar to ATC fuses despite them being much larger than ATC fuses. Available in amperages ranging from 30 amps up to 80 amps, these fuses are a solid choice when a predictable time delay is a benefit. Another benefit of these fuses is their rapid installation time.

MRBF
Marine rated battery fuses are commonly used in ignition protection circuits and are used in conjunction with terminal blocks. This type of fuse is available in amperages ranging from 30 amps all the way up to 300 amps giving you the needed protection for your application.

Class T
Class T fuses, like many of the fuses on this list, are known for their fast-acting design. This type of fuse specializes in preventing short circuits and offers 20,000 amp interrupting capacity. Often, you will find Class T fuses in use protecting panel boards and other important pieces of electrical equipment.
What is the difference between these fuses?
These fuses vary in a few major ways. The first and most obvious difference between these fuses is the body shape and size. Of course, different applications have different needs which leads to different fuse blocks and fuses. Having different fuse block types makes perfect sense. This is why it is vitally important to pay attention to the exact style of fuse that you are planning to order. The last thing you want is to discover that you have a different fuse block than you thought. The second major difference between these fuses is the amperage that they can tolerate. Some do not go past 30 amps while others go beyond 100 amps. So that leads us to the next question, how do you know which type to use?
How do I know which fuse to use?

The biggest deciding factor on which fuse to get is the amperage. As we said above, some types of fuses top out at a low amperage. If you need a 60-amp fuse, then you can skip right over AGC and ATC fuses. Once you know the amperage that you need, the next step depends on whether you are replacing an existing fuse or installing a new fuse and fuse block. If just replacing a fuse, then your choices are narrowed since the fuse needs to fit the existing fuse block. If you are doing a new install, then you can choose the fuses and fuse block that best suits the specifics of the application.
Where would I use a fuse block?
You would want to install a fuse block in any electrical circuit where you have multiple pieces of electrical equipment to protect from any over current. The best part about a fuse block is that it offers protection for multiple pieces of electronic equipment simultaneously. In this way, a fuse block is the superior method when it comes to integrating fuses into an electrical system.
How do I know what fuse block to use?

The first thing to look at when considering which fuse block to use is which type of fuses are best suited for your application. This may seem obvious but often we have people looking for a fuse block based on amperage but are unsure as to which type of fuse they are going to use. Once you know the type of fuse you intend to use, the next step is to select the fuse block that best suits your amperage needs. By selecting the amperage last, you eliminate a lot of the selection since, to some degree, they share amperages. This makes your final choice that much easier.
What are fuse holders?

Fuse holders are specialized devices that integrate a fuse into an electrical circuit where there is not already a place for that fuse. What we mean is that a fuse holder will allow you to add a fuse to an electrical circuit without some complex workaround. Fuse holders are easy to install and maintain making them an ideal solution for field service.
How is a fuse holder different from a fuse block?
A fuse holder is designed to handle a single fuse and is often installed inline. This is vastly different from a fuse block where you have a large device that holds up to twelve different fuses. Another way to look at it is that a fuse holder is commonly used for more simplistic circuits whereas a fuse block is better suited for a more complex electrical circuit. It's simple to tell a fuse holder from a fuse block once you know what to look for.
Fuse holders hold a single fuse
![]()
A fuse block holds multiple fuses
*This page was updated on 8/1/2022*




